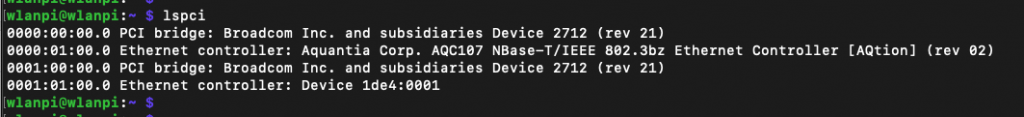
This journey started as an exploration of maximum PCIe capabilities of Raspberry Pi 5 (and hopefully Compute Module 5) platform. I am mainly interested in multi-gigabit Ethernet and Wi-Fi 7 adapters connected via the PCI Express (PCIe) x1 bus.
Last time, we got throughput of 3.44 Gbps. The adapter and the Pi hit the bottleneck of PCIe Gen 2. Unfortunately, they failed to establish PCIe Gen 3 mode.
Generic 10 GbE adapter in M.2 form factor
This time we are going to use a slightly different adapter. It is available from various sellers under different names, but they all look and work the same. I picked up one from “KALEA-INFORMATIQUE” which happened to be readily available in the UK.
Pineberry’s HatDrive! Bottom breaks out Raspberry Pi’s PCIe connection to M.2 M-key format, and that’s where this 10 Gigabit Ethernet adapter plugs into.
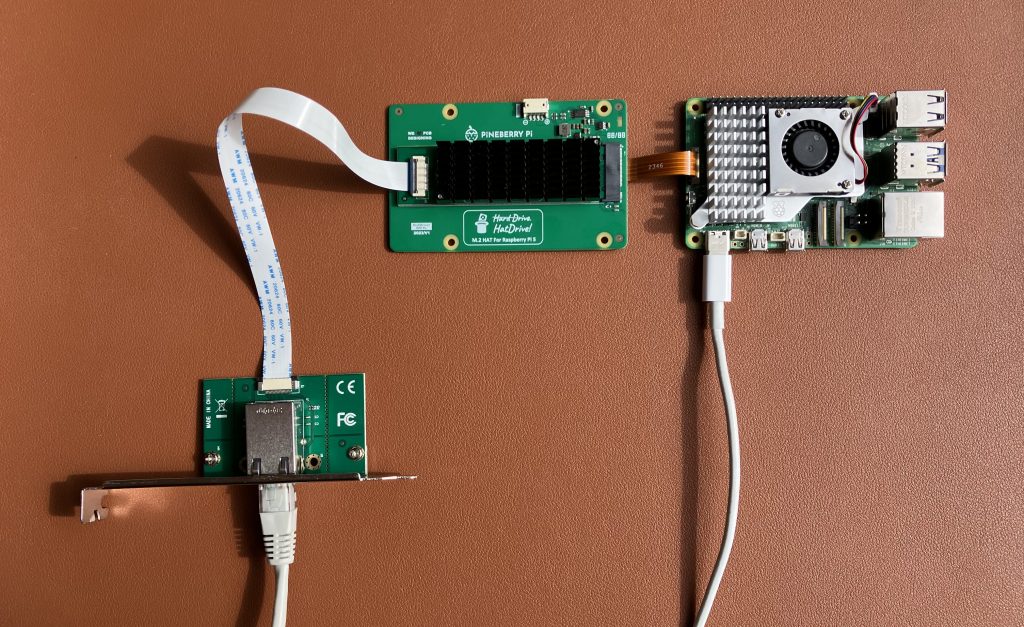


Build custom kernel with AQC107 support
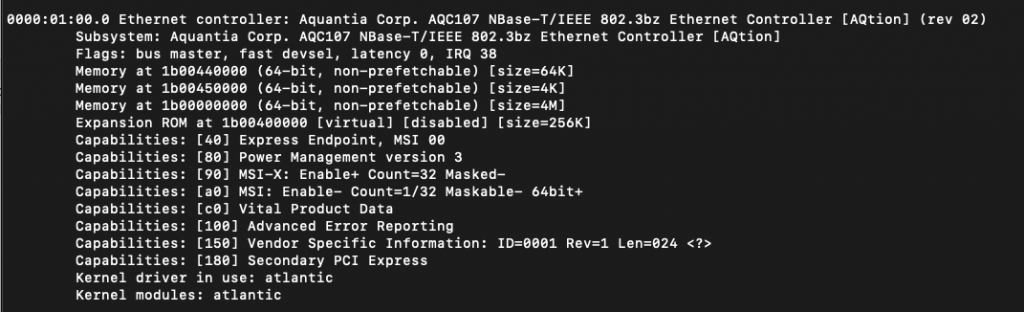
This Ethernet adapter uses the same chip and driver the one we previously tested. Here are the steps to make compile a custom Linux kernel that supports the adapter.
Wait, why is it still not working?
We have connected everything, built a custom kernel, we can see the device, but the Ethernet interface is not coming up.
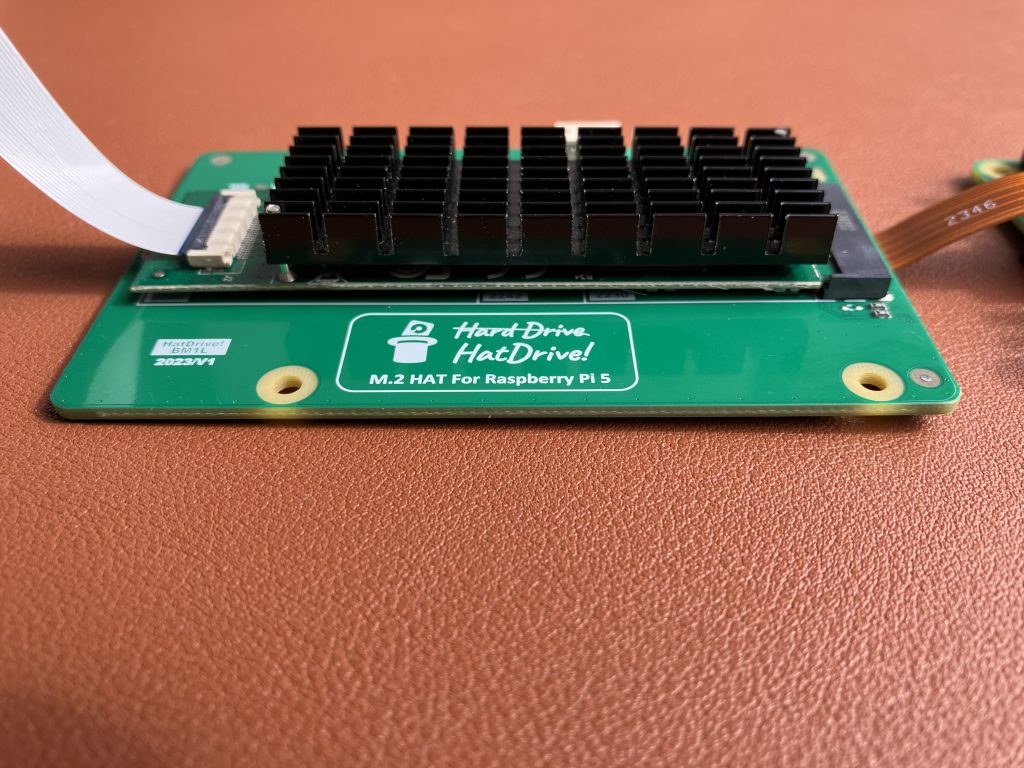
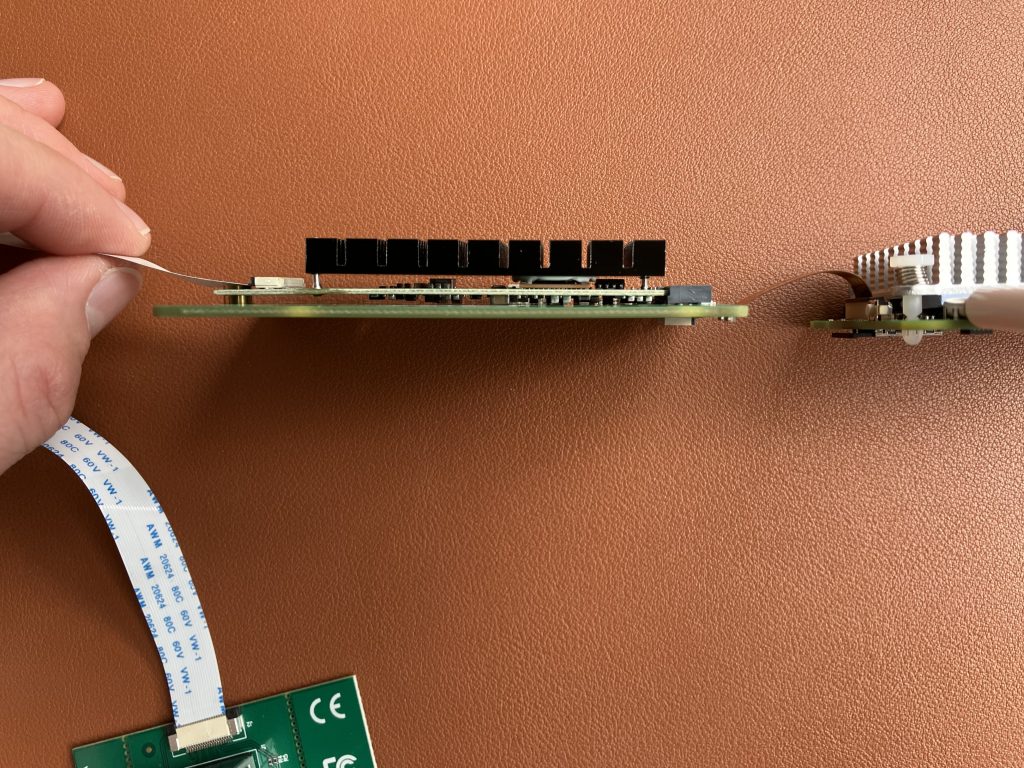
Look at this official product photo and my photo below. Spot one difference 😉


Did you notice the orientation of the white ribbon cable? The official photo got it wrong. The printed text on the cable needs to be on the top on one side, and on the bottom on the other one.
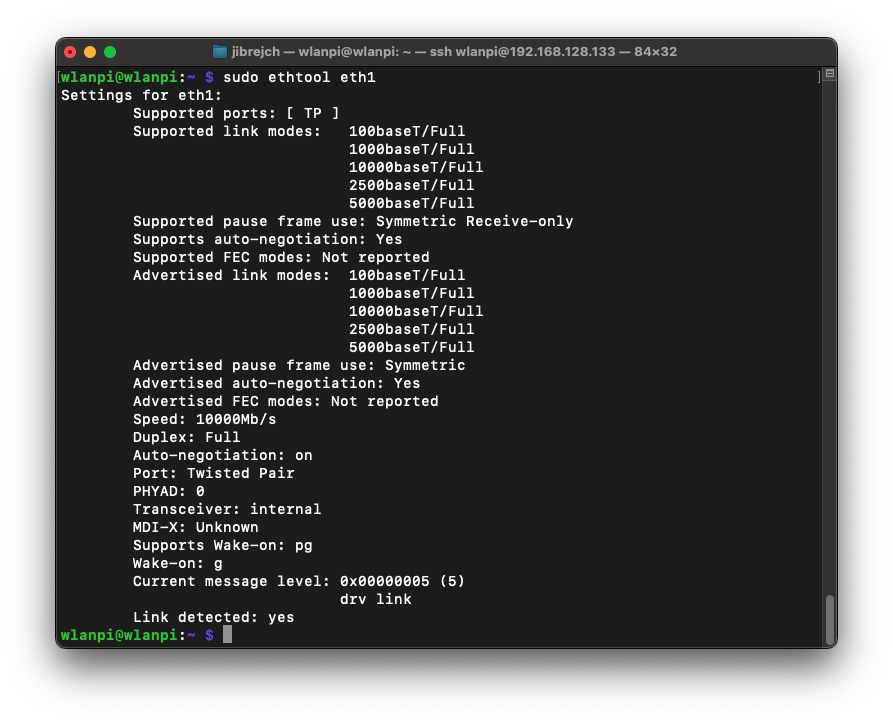
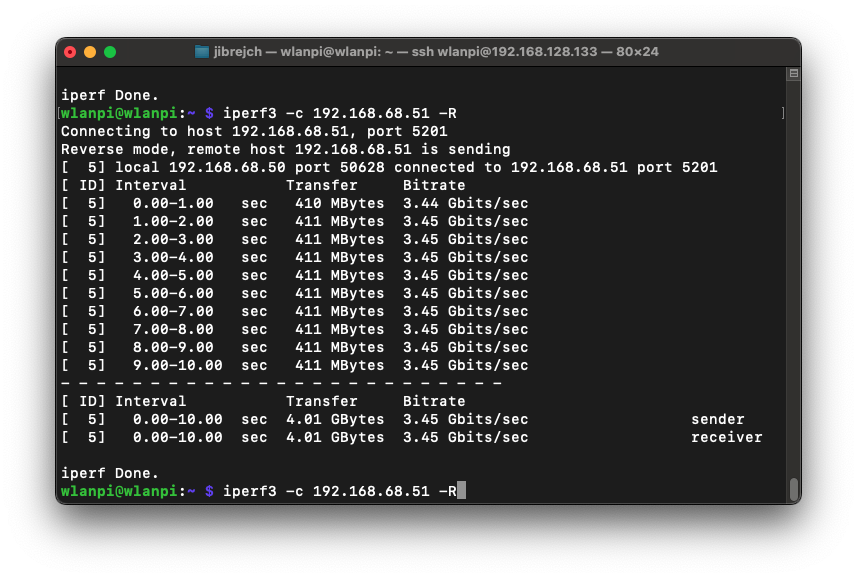
What speeds did you get in PCIe Gen 2 mode?
After correcting the orientation of the flexible cable, the interface came up, negotiated 10 Gbps full duplex.
I started throughput testing against MacBook with my trusty 10 GbE Thunderbolt adapter.
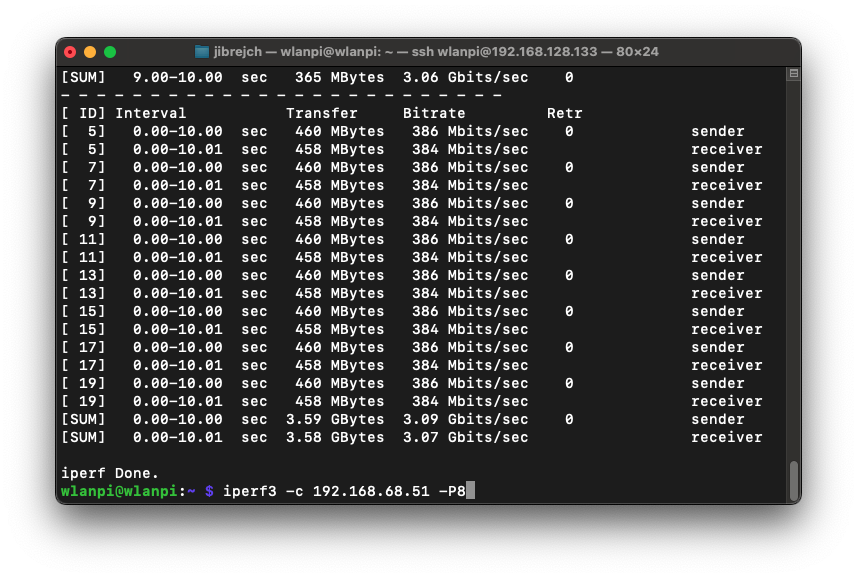
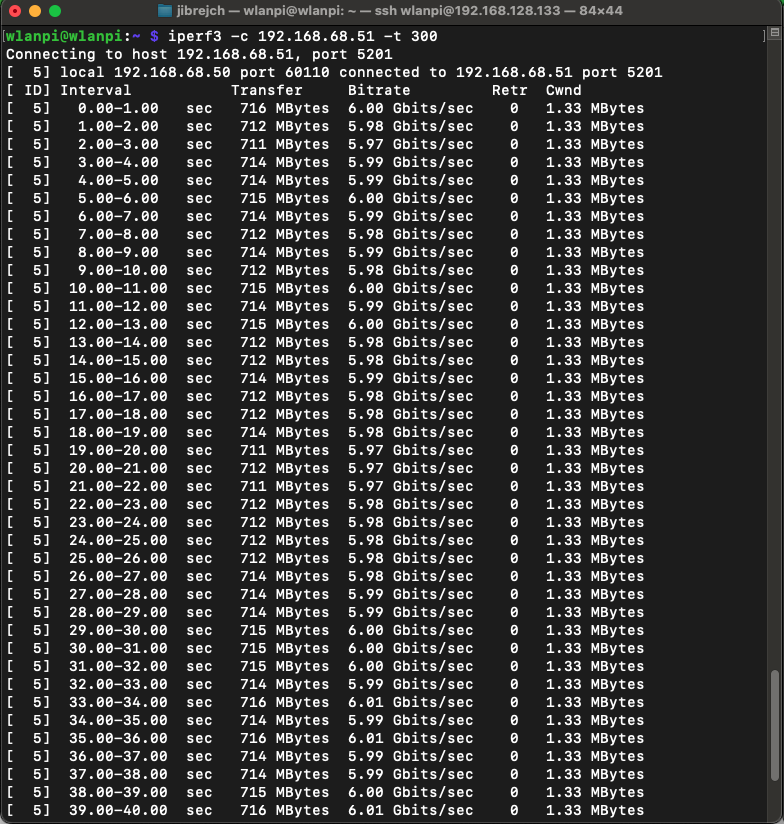
In PCIe Gen 2 mode, we got TCP throughput of 3.45 Gbps on the downlink and 3.07 Gbps in the upstream direction. Using more iperf3 parallel streams did not increase performance.
Were you able to use PCIe Gen 3 mode?
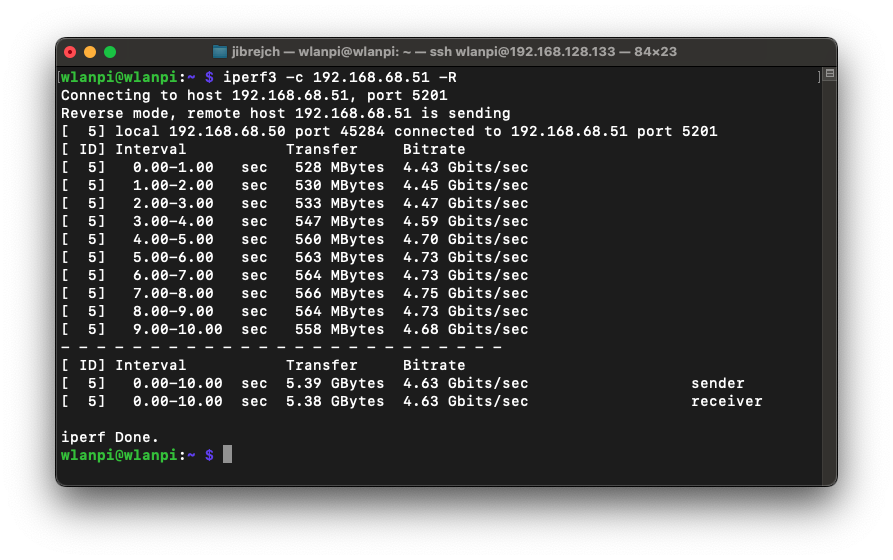
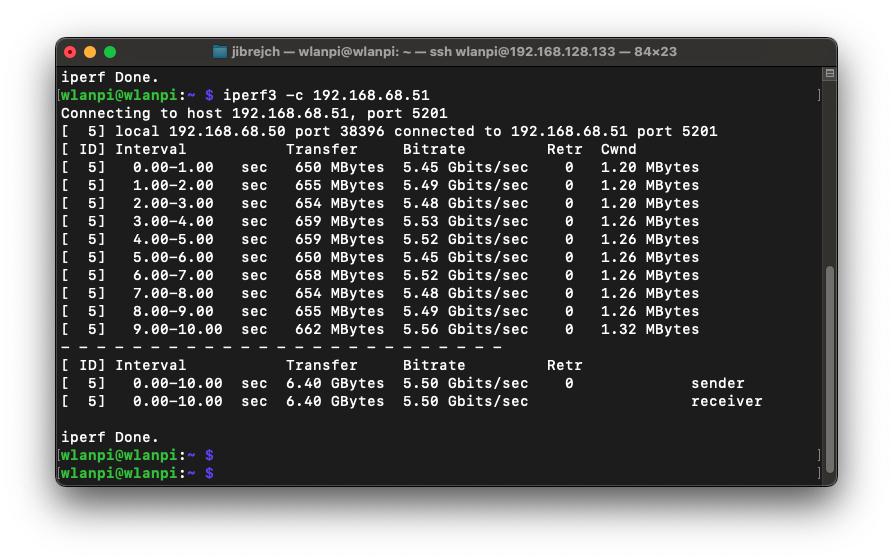
Yes! And I got 4.63 Gbps of TCP downstream and 5.5 Gbps (potentially up to 6 Gbps) upstream.
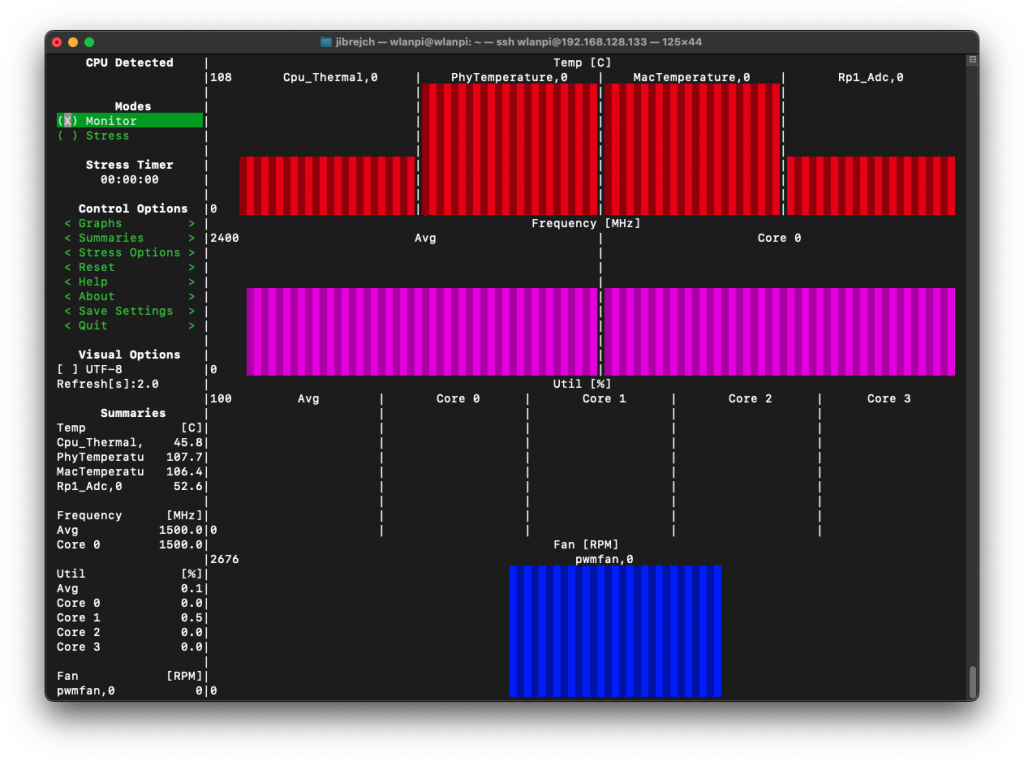
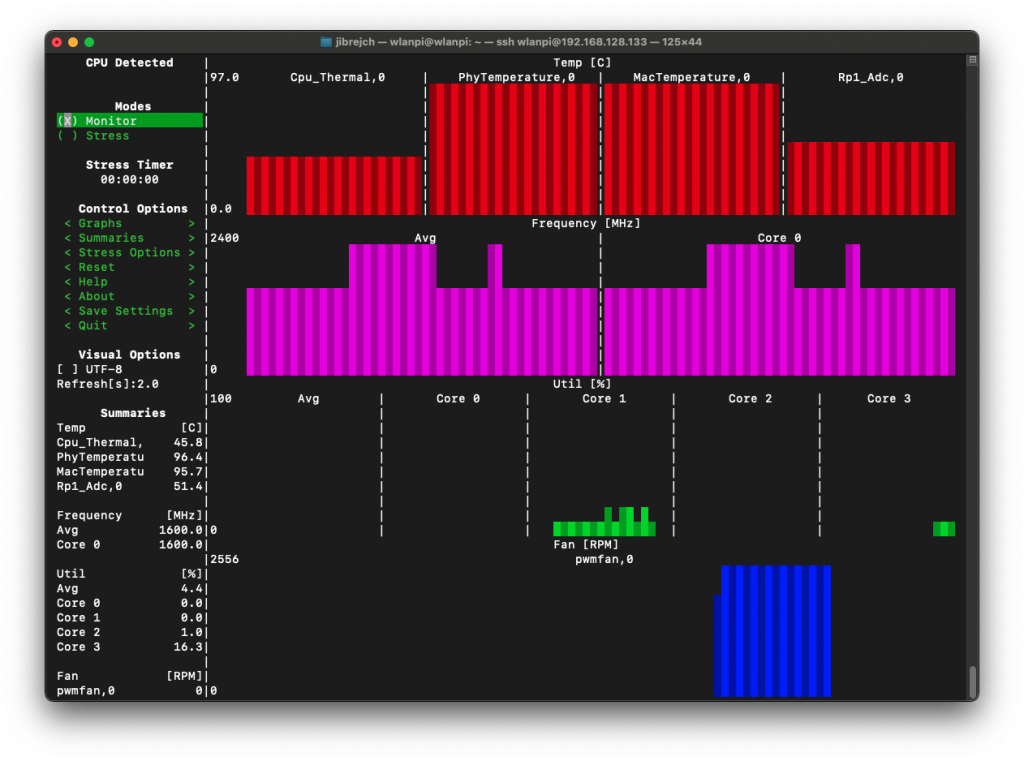
That’s hot news… yes 122° Celsius hot!
This adapter has a thermal problem. It comes with a heatsink, but even in idle mode it overheats.
In PCIe Gen 3 mode with iperf3 test running, we are talking 122.1° C hot! The Pineberry board was very hot and you can literally burn your fingers by touching the heatsink.
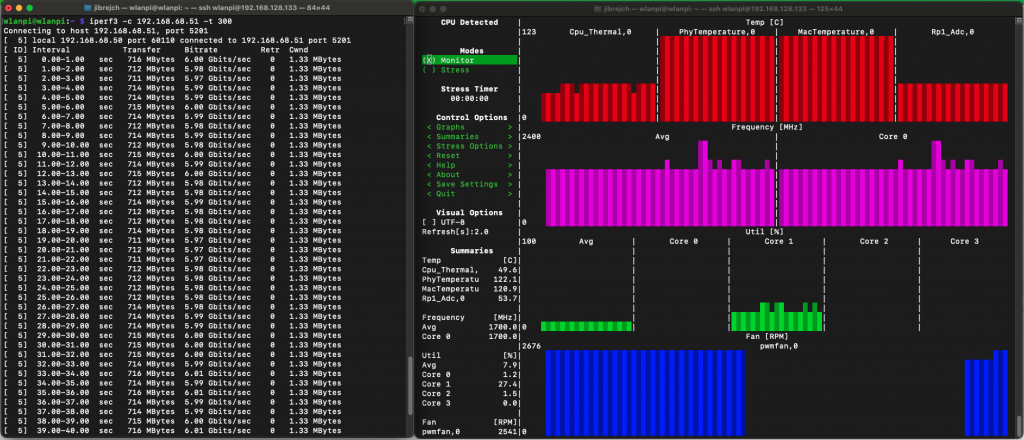
Long story short. Don’t buy this adapter, unless you want to add a fan or significantly larger heatsink.
Toaster, 10 Gigabit adapter, aren’t they the same thing?
Make your own opinion based on these couple of thermal photos.
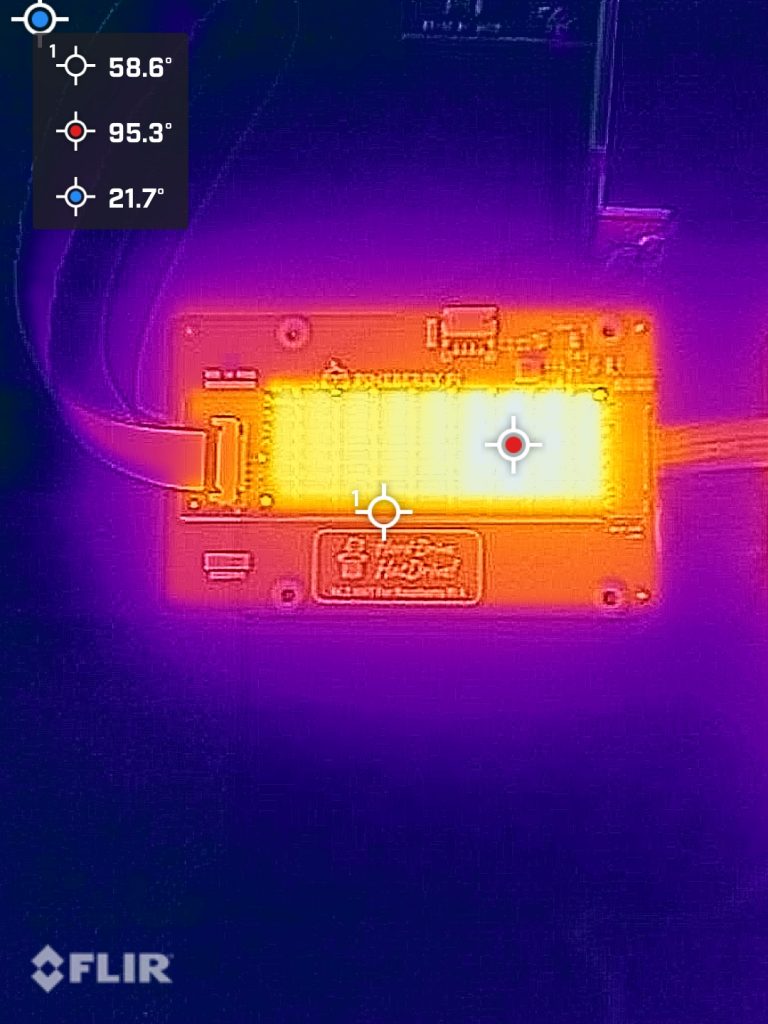
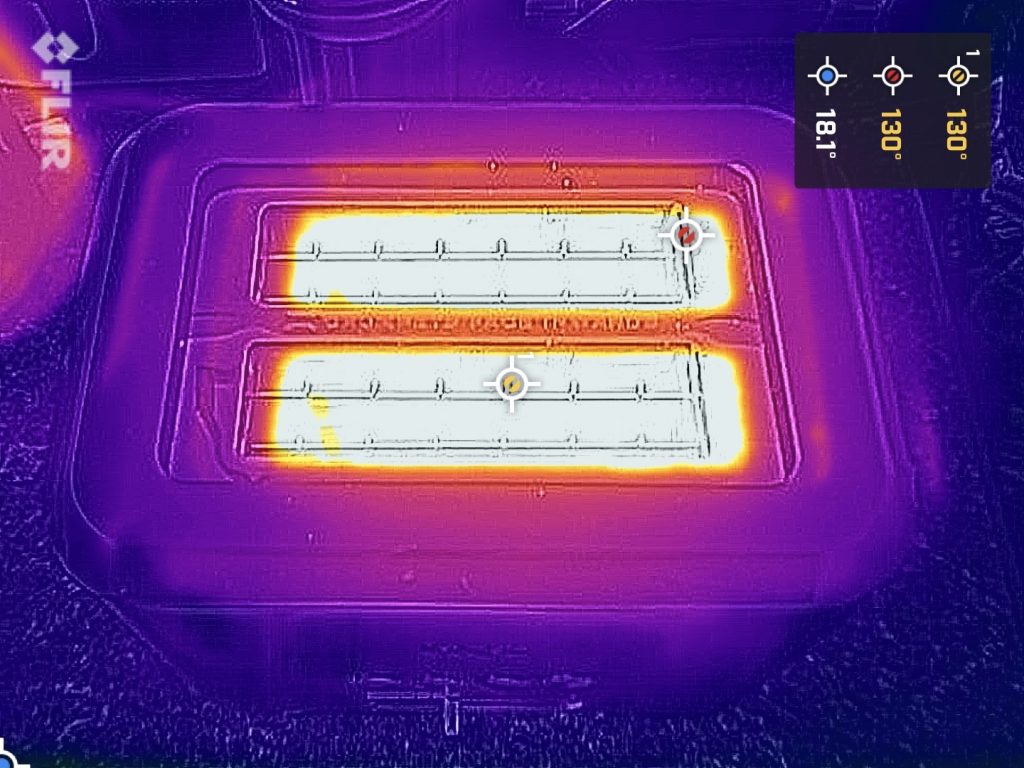
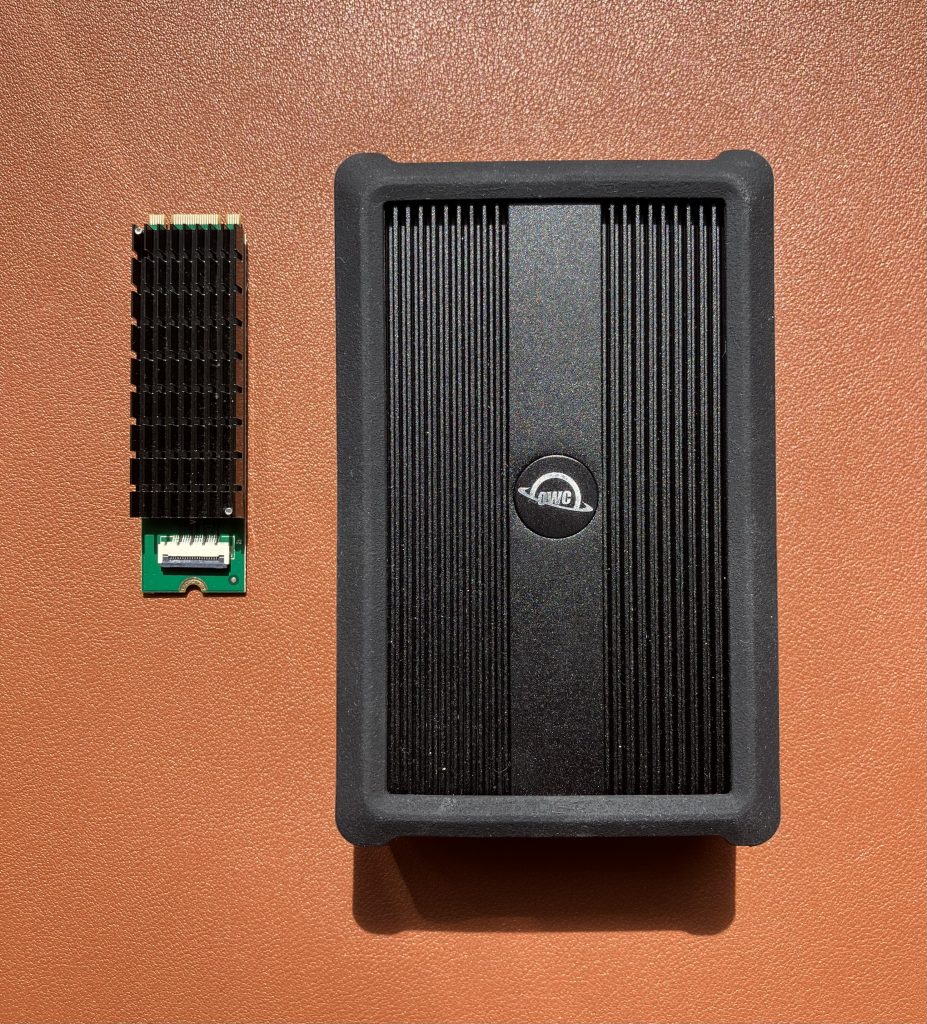
This Ethernet adapter as well as the OWC 10 GbE Thunderbolt both use the same Aquantia AQC107 (part of Marvell now) chip. It does really good job at keeping CPU utilisation low. I’ve seen much cheaper 2.5 GbE adapters that hammer CPU with interrupts until the CPU just can’t take no more.
But, compare size of the two heatsinks. Unlike this one, the OWC adapters delivers good thermal results. Don’t take me wrong, it still runs warm, but not anywhere near.

Summary
On the positive side, this is the first 10 Gigabit adapter I tested which actually worked in PCIe Gen 3 mode on Raspberry Pi 5. I got TCP throughput of up to 6.0 Gbps.
As far as I can tell, the limit of Raspberry Pi 5’s PCIe bus is around 6 Gbps if you look at it through the iperf3 TCP traffic lens. AQC107 silicon does an amazing job at keeping the Raspberry Pi’s CPU utilisation low. This helps us get as much throughput as we can from the Pi. But it produces a significant amount of heat.
The fact is that this adapter overheats. Don’t buy it unless you wish to use it with a fan or design a much larger heatsink yourself.