Earlier this week, I tested a 10 Gigabit Ethernet M.2 network adapter on Raspberry Pi 5, and it didn’t quite cut it. Mainly due to limited PCIe Gen 2 performance. Now, the question is can this 10 Gigabit adapter actually push 10 Gbps of traffic at all?
To find out, we are going to slightly reconfigure this Intel NUC 12th generation mini PC. It has an M.2 M-key slot for NVMe drive. Let’s use this slot for our 10 GbE adapter. And we will boot Windows 11 off an external USB SSD drive.
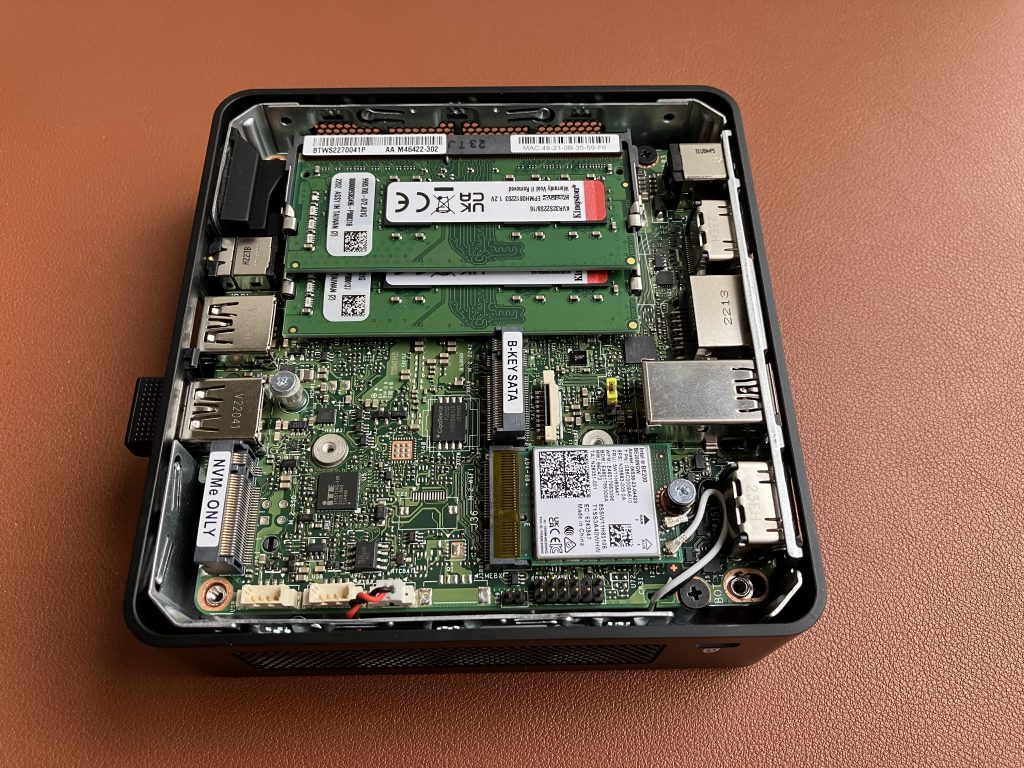
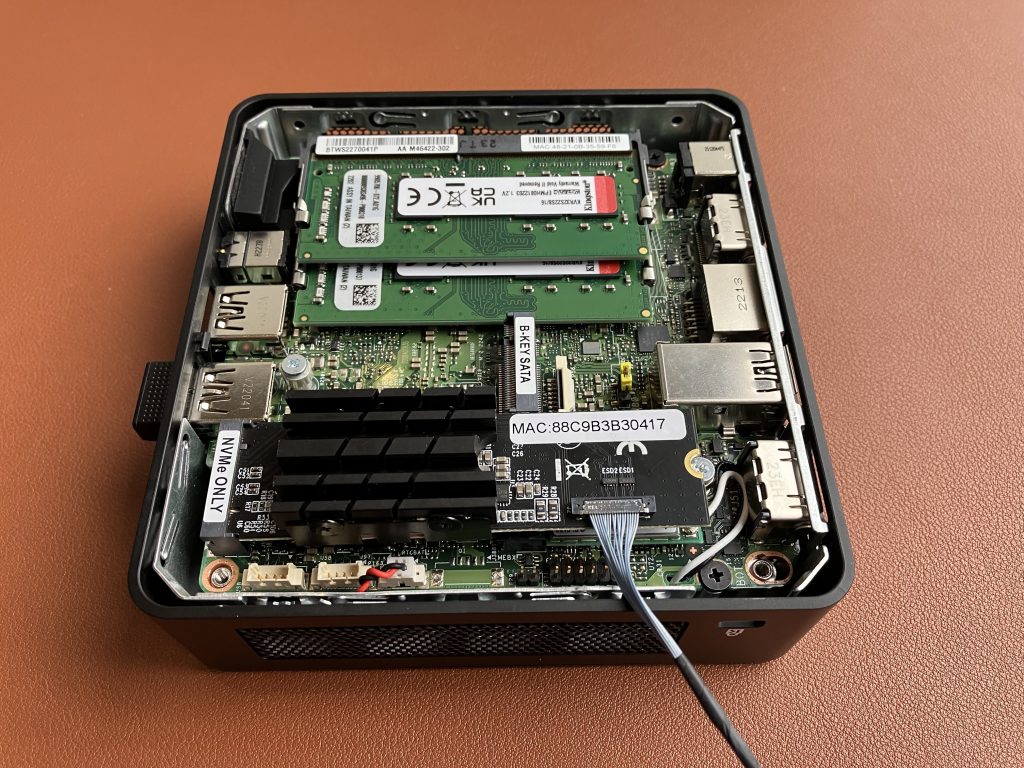
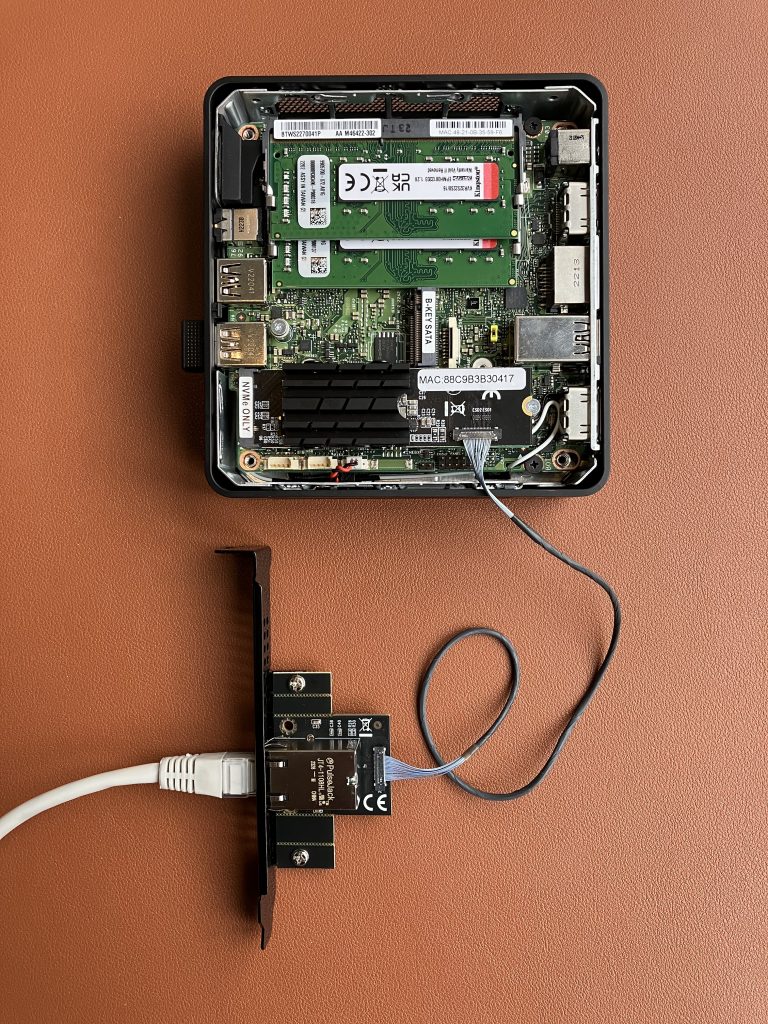



Install Windows 11 23H2 version on a USB SSD drive, boot Windows, run Windows Update, voila!
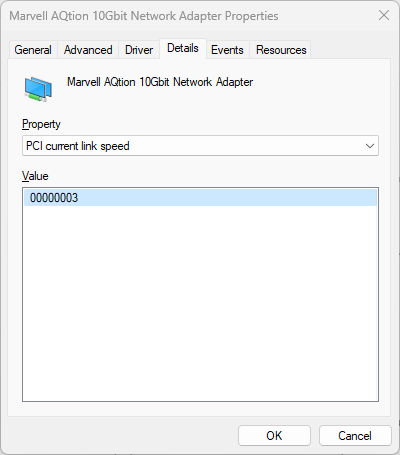
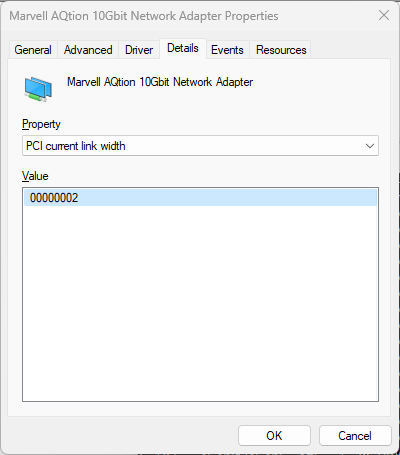
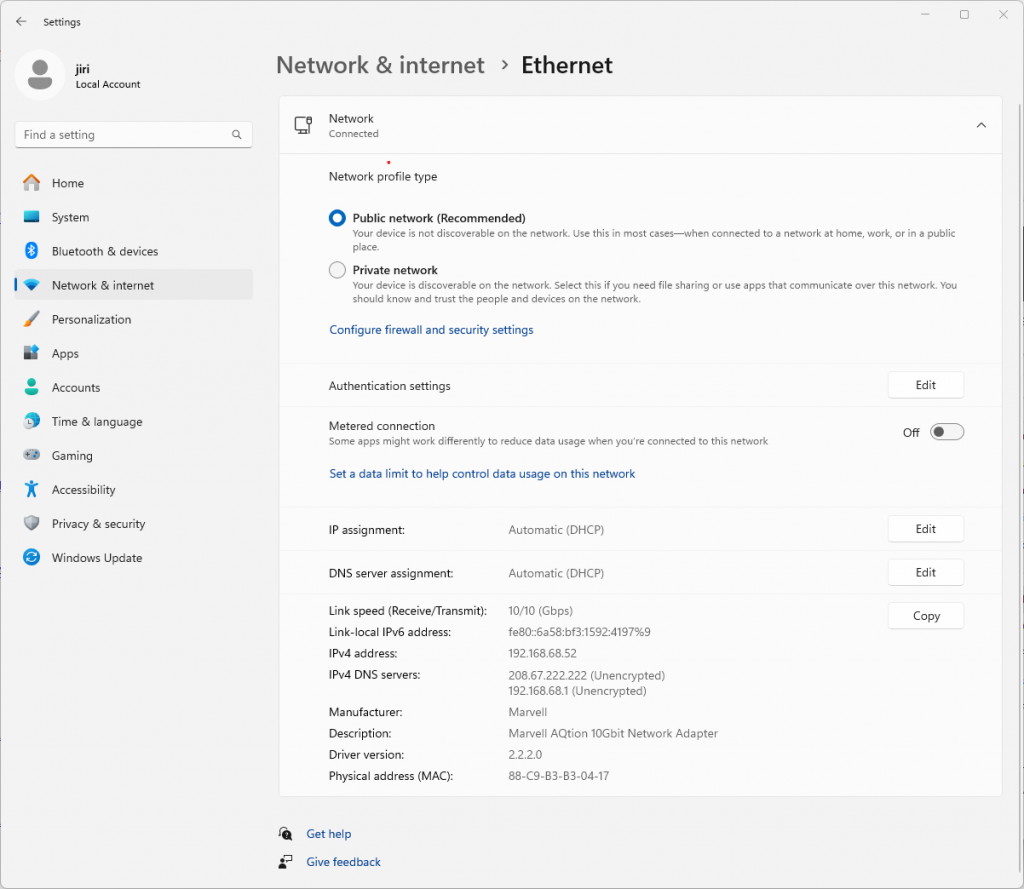
With default iperf3 settings we get 6.44 Gbps/7.93 Gbps in the downlink and uplink direction respectively. Not bad, but is that it? Of course not.
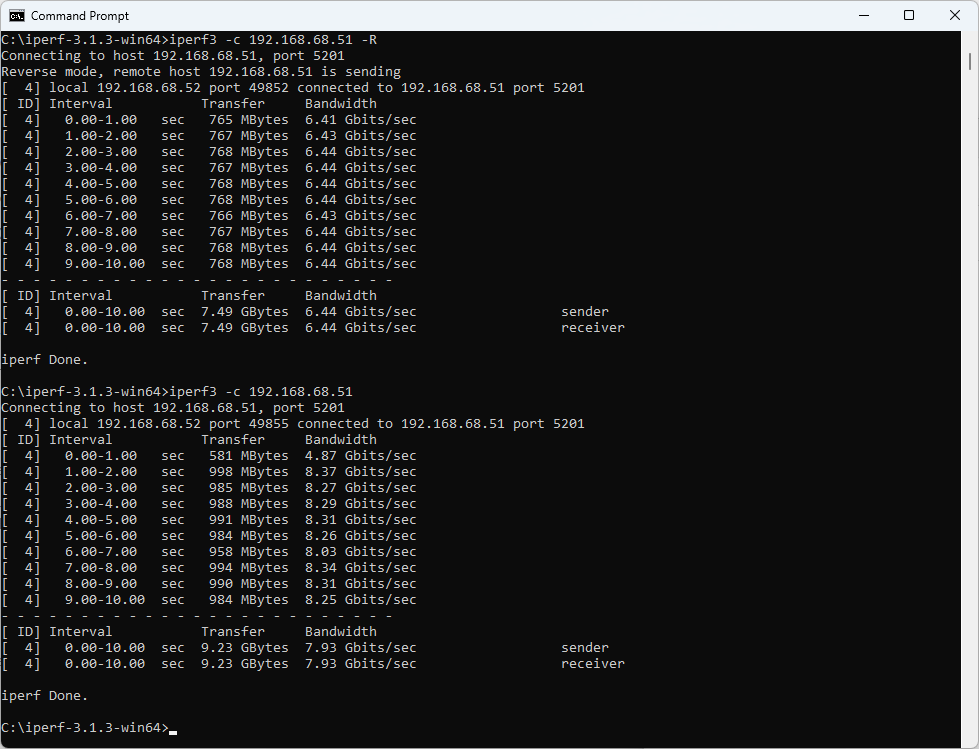
I don’t really want to enable Jumbo frames as it’s not always possible to enable Jumbo frame support end-to-end, especially if part of the network doesn’t support it or isn’t under your management. Fortunately, 8 parallel TCP streams in iperf3 do the trick for us. We get 9.48 Gbps download speed.
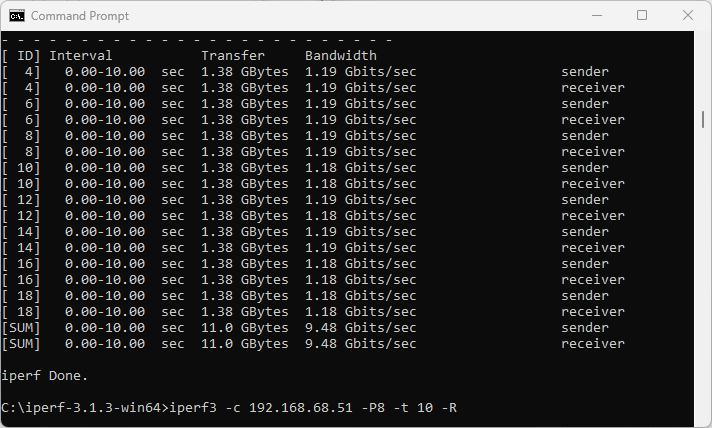
In the upstream direction from this NUC to my MacBook with 10 GbE adapter, we also get 9.48 Gbps. I am happy. You? 😉
Summary
After all, this 10 GbE M.2 network adapter is indeed capable of pushing 9.48 Gbps of traffic in either direction. But! It is not really a good choice for a system like Intel NUC. I can’t pop the lid back on, the heatsink is too tall. Frankly, I can’t recommend this adapter at all. It runs hot at 84° Celsius in idle.
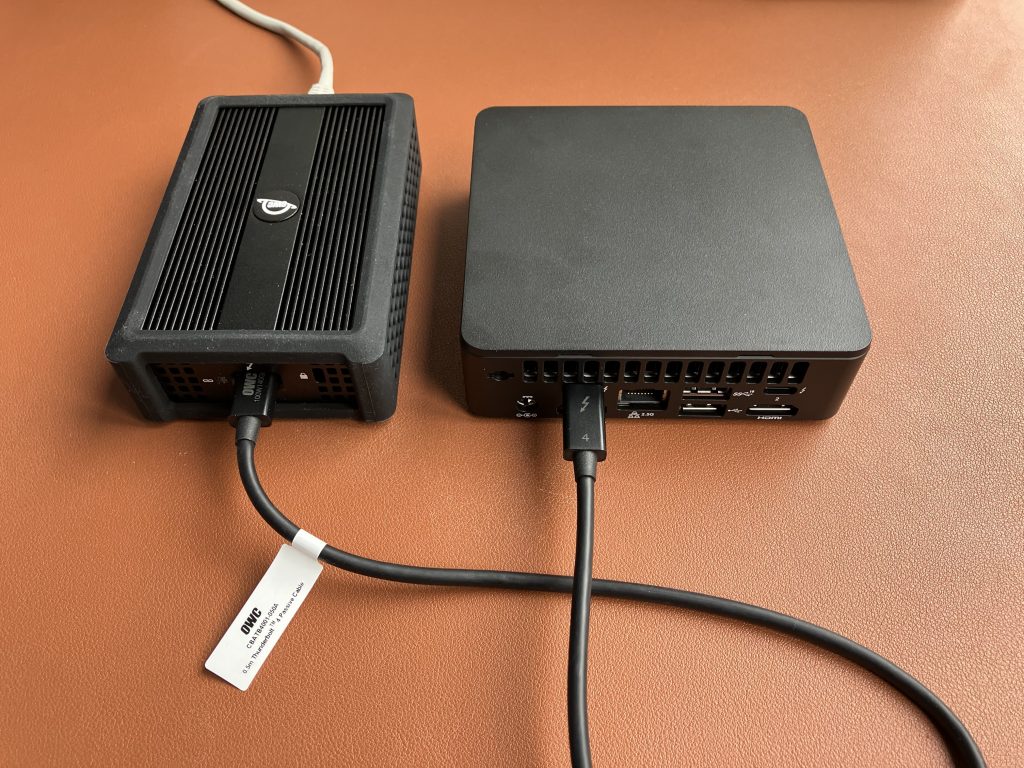
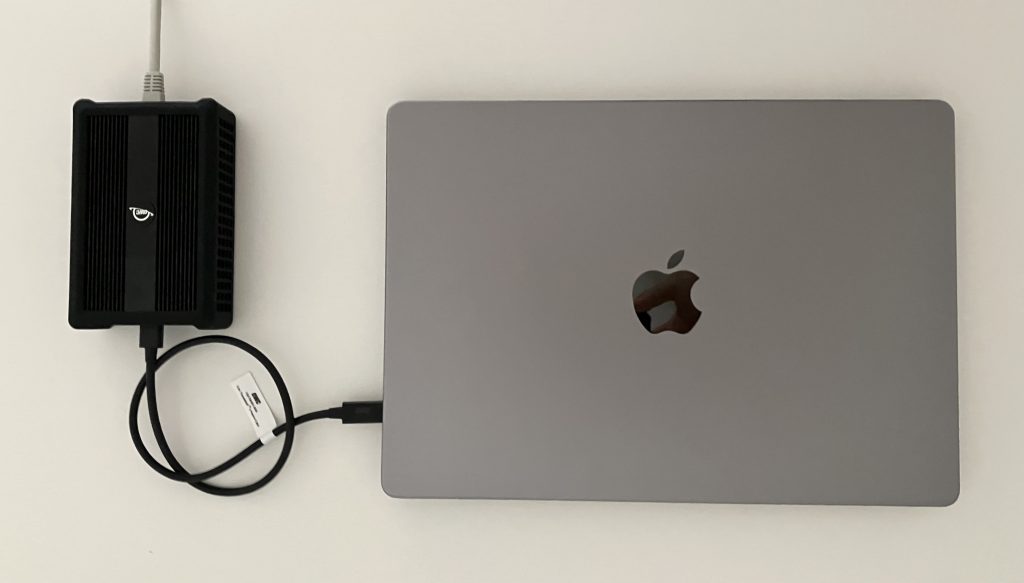
If you are looking for a daily driver, and your system supports Thunderbolt, get yourself this OWC 10GbE to Thunderbolt adapter. Here is my test. It works out of the box on Windows (I tested this Intel NUC 12th Gen) and macOS (I tested MacBook Pro M1 and M2). Interestingly, it uses the same chip as the above M.2 adapter. Just compare the two products and their heatsink sizes. The AQC107 keeps the main CPU utilisation very low, but it produces a significant amount of heat.

